Full-text search in ANNO
3. Navigation within the search results
4. Refining the search results
5. Specific features of the ANNO search-mode
1. General information
1.1 Indexed inventory of newspapers
The full-text search is still being developed and doesn't yet include the whole inventory of digitised newspapers and magazines in ANNO yet. However, according to the current status, more than 90% of our digital collection is searchable.
1.2 Quality of full-text
The full-text is based on OCR data. OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is an automated process. For this reason, a high error rate may occur in some texts. Therefore, in some cases, a manual search may return different results. To minimize this limitation, the use of wildcards could be helpful.
1.3 How to request the full-texts
In ANNO, there is the option to view the full-text of every single page. For this purpose there is a "text"-Button on the upper right of the screen in the single view of every page of newspapers and magazines, which have already been OCR-read.
2. Begin your search
2.1 Simple search
You can search for particular terms in newspaper issues via the simple search ("Einfache Suche"). Refining the search is possible using Boolean operators, wildcards and phrases (see 4. refining the search results).
After typing search terms, click "Enter" or click on the magnifying glass symbol, the search will begin. Search results will be displayed according to relevance. Furthermore, you can switch to the advanced search ("Erweiterte Suche") by clicking on the drop-down menu to the left of the search box. The button "ANNO-Suche" deletes your previous entries and leads you back to the homepage of the search engine.
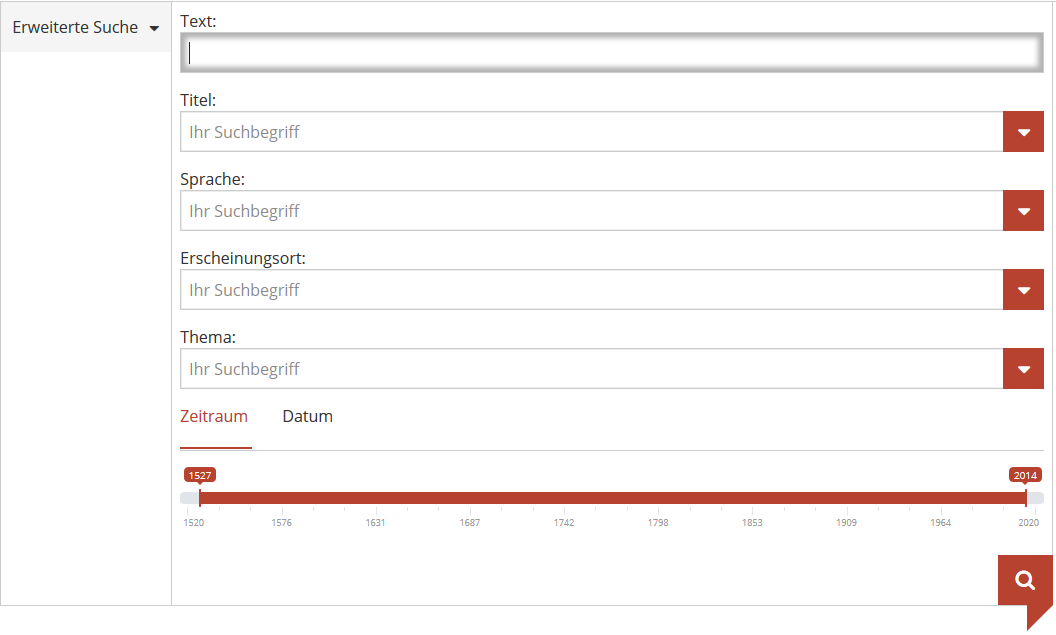
2.2 Advanced search
Different categories can be filtered in an advanced search. These include the title of a newspaper or a journal, language, place of publication, topic and/or from-to date.
Search box "Text" (text): Enter search term(s). As in the simple search, it is possible to use Boolean operators, wildcards and phrases here.
Search box "Titel, Sprache, Erscheinungsort" (title, language, place of publication): Enter term or select one from the drop-down menu by clicking on the red button to the right of the search box.
Search box "Thema" (subject): Select a subject from the drop-down menu. Every title in ANNO has at least one subject classification. The categories follow a fixed vocabulary, which is used in library cataogues.
Search box "Datum" (date): There are two ways to conduct a date search. 1) Choose an interval of years by clicking on "Zeitraum" or timeframe. Using the timeline provided just below this option, set the date parameters. 2) Search by date by clicking on "Datum." Enter either a starting point only, which will search all newspapers and magazines from that date onward. Or, enter both a start and end date to search a specific timeframe. Use either the calendar icon provided "von" from/ "bis" until, or enter date using the following format: DD.MM.YYYY
3. Navigation within the search results
3.1 List view of the search results
The list view shows results of the search, by issue, ranked by the number of times the search term was found within that issue. There is a red navigation bar at the top of the page to move through results. By clicking on the "Treffer im Text" by each cover icon, a preview of matching text snippets that are in that issue will appear. To see the entire issue, click on the cover icon itself. For search terms that generate over 500,000 results, the system may take a moment to list.
To limit the scope of a search, there are six filters provided to the left of the list view:
-
Medium
-
Title
-
Publishing Location
-
Language
-
Timeframe
-
Subject
Within each filter, there are up to 10 filter options. Please note: for more specialized searches, it is recommened to use the "Advanced Search" option instead of the provided filters. To do this, choose "Erweiterte Suche" to the left of the search box at the top of page.
3.2 Sorting
Search results can be arranged by using the drop-down menu next to the navigation bar. In the default setting, the results are sorted by relevance. It is also possible to sort by publication date or title (both ascending on descending) as well as by titles which have been most recently added to the index.
3.3 Filter
As mentioned above, there are filters provided to the left of the hit list to enable a restriction of the scope of your search results. These are grouped by medium, title, place of publication, language, time intervall and topic. Every group contains a maximum of ten filters. The number of hits is shown next to the name of every particular parameter.
The active filter is shown above the filter list (not above the results). Active filters can be deactivated by clicking on them. Doing so will show the complete result list again.
3.4 Navigating search results
There are three ways to navigate results. By clicking on the thumbnail, the title of the issue, or the number of hits.
Open in ANNO
If you click on the thumbnail or on the title of the issue, the complete issue containing the hit(s) displays in a new tab. The pages with hits are bordered in red. Additionally, a gray information bar with your search term and the number of hits is shown directly below the header.
Preview
The third option is to click on the number of hits. If you do so, a list of cut-outs with hits displays and you can navigate directly to these pages in the issue. This option allows you to check in advance if the hit is really relevant for your research. Words, which have been identified as a hit, are highlighted in red.
4. Refining the search results
4.1 Boolean operators
The Boolean operators allow you to refine your search in the simple search mode. Therefore, if you wish to search for issues containing the word Hofbibliothek but not Sonntag, is it possible to carry out this search by entering Hofbibliothek NOT Sonntag. The operators always have to be written in English and in capital letters. In the default setting, search terms without a Boolean operator are connected by a logical AND.
4.2 Wildcards
Wildcards are placeholders for any kind of characters. The asterisk (*) is available in the ANNO-search for an unlimited number of characters. The question mark (?) substitutes only one character. For example, if you wish to search for the term Balthazar, but also want the spelling Balthasar to be included, you can simply enter Baltha?ar. However a search for Baltha??r considers spellings such as Balthasar and Balthazár. Please be aware, that the question mark(s) can be replaced by any other character as well.
The same applies to the asterisk, which replaces many characters. A search for Kro* can deliver hits like Krone or Krokus. Use of the character * is only supported when at least three non-wildcard characters are put in front of it. For instance, a valid search would look like Baltha*, Bib*, Ste*en. Examples of invalid searches would be *, Ba*, *rreich.
Using the character ? also requires at least three non-wildcard characters in front of it. Valid search terms, for example, would be Ka?ser, die?? , w??der. Likewise, search terms such as Ka? , ?eder would be invalid.
4.3 Phrase search
A phrase search enables users to search for exact phrases. A phrase is created by placing two or more words within quotation marks ("). While for example, a search for Ferdinand Balthasar yields all issues with the individual words Ferdinand and Balthasar in any position, (e. g. ... Erzherzog Ferdinand ... Balthasar III. Freiherr ...), a phrase search for "Ferdinand Balthasar" limits the search results to issues where these two words occur exactly next to each other.
It is also possible to combine a phrase search with a wildcard search. For example, searching for "Erzherzog Ferdinand" Thom? provides hits in issues which include both the phrase and the term with a wildcard. Wildcard characters cannot be used within quotation marks.
4.4 Proximity Search
The proximity search allows you to reduce the number of hits. By entering "Ferdinand Balthazar"~17 you only allow an occurance of a maximum of 17 words between "Ferdinand" and "Balthazar". The order of the words "Ferdinand" and "Balthazar" is not taken into account by this search query. Therefore, occurrences of "Balthazar" … "Ferdinand" will be found as well. The minimum distance you can search for is one word.
5. Specific features of the ANNO search-mode
The search engine opens ANNO in a special mode. The usual view of the ANNO-page is supplemented by an information bar of the ANNO search engine. The current search term(s) and the number of hits are displayed in the gray information bar directly below the header.
The search query is retained while navigating between the pages of a particular issue. In case you switch to another issue or to the calendar-view, will the query be discarded and you will be directed to the normal ANNO-view again.
6. Saving search queries
The search queries in ANNO can be saved as a bookmark for subsequent research. Specific search queries (pages, issues) can be bookmarked.